Creating an ECS cluster with Terraform
AWS introduced dynamic port mapping for ECS around 18 months ago. This is a very useful feature that allows you to run multiple containers with the same port on the same host. This feature is only avaliable with the AWS application load balancer. The ALB automatically detects and reconfigures itself to map to a port inbetween 32768 and 65535.
So let’s automate creating an ECS cluster with Terraform.
You can also find the code at my GitHub HERE.
First let’s set up our provider
provider.tf
provider "aws" {
profile = "default"
region = "${var.aws_region}"
}
We then have the file that creates a new VPC
vpc.tf
### Network
# Internet VPC
resource "aws_vpc" "demo-tf" {
cidr_block = "172.21.0.0/16"
instance_tenancy = "default"
enable_dns_support = "true"
enable_dns_hostnames = "true"
enable_classiclink = "false"
tags = {
Name = "demo-terraform"
}
}
# Subnets
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-public-1" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.10.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "true"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2a"
tags = {
Name = "demo-public-1"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-public-2" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.20.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "true"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2b"
tags = {
Name = "demo-public-2"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-public-3" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.30.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "true"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2c"
tags = {
Name = "demo-public-3"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-private-1" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.40.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "false"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2a"
tags = {
Name = "demo-private-1"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-private-2" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.50.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "false"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2b"
tags = {
Name = "demo-private-2"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "demo-private-3" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
cidr_block = "172.21.60.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = "false"
availability_zone = "eu-west-2c"
tags = {
Name = "demo-private-3"
}
}
# Internet GW
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "demo-gw" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
tags = {
Name = "demo-IG"
}
}
# route tables
resource "aws_route_table" "demo-public" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = "${aws_internet_gateway.demo-gw.id}"
}
tags = {
Name = "demo-public-1"
}
}
# route associations public
resource "aws_route_table_association" "demo-public-1-a" {
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.demo-public-1.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.demo-public.id}"
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "demo-public-2-a" {
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.demo-public-2.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.demo-public.id}"
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "demo-public-3-a" {
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.demo-public-3.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.demo-public.id}"
}
Next we have our configuration for the Application Load Balancer
alb.tf
## ALB
resource "aws_alb" "demo_eu_alb" {
name = "demo-eu-alb"
subnets = ["${aws_subnet.demo-public-1.id}", "${aws_subnet.demo-public-2.id}", "${aws_subnet.demo-public-3.id}"]
security_groups = ["${aws_security_group.lb_sg.id}"]
enable_http2 = "true"
idle_timeout = 600
}
output "alb_output" {
value = "${aws_alb.demo_eu_alb.dns_name}"
}
resource "aws_alb_listener" "front_end" {
load_balancer_arn = "${aws_alb.demo_eu_alb.id}"
port = "80"
protocol = "HTTP"
default_action {
target_group_arn = "${aws_alb_target_group.nginx.id}"
type = "forward"
}
}
resource "aws_alb_target_group" "nginx" {
name = "nginx"
port = 80
protocol = "HTTP"
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
depends_on = ["aws_alb.demo_eu_alb"]
stickiness {
type = "lb_cookie"
cookie_duration = 86400
}
health_check {
path = "/"
healthy_threshold = 2
unhealthy_threshold = 10
timeout = 60
interval = 300
matcher = "200,301,302"
}
}
Next we set the AMI we use and update the launch configuration of the cluster
data.tf
# Get the latest ECS AMI
data "aws_ami" "latest_ecs" {
most_recent = true
filter {
name = "name"
values = ["*amazon-ecs-optimized"]
}
filter {
name = "virtualization-type"
values = ["hvm"]
}
owners = ["591542846629"] # AWS
}
# User data for ECS cluster
data "template_file" "ecs-cluster" {
template = "${file("ecs-cluster.tpl")}"
vars = {
ecs_cluster = "${aws_ecs_cluster.demo.name}"
}
}
Next we add the configuration for our ECS cluster
ecs-cluster.tf
# ECS cluster
resource "aws_ecs_cluster" "demo" {
name = "demo"
}
#Compute
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "demo-cluster" {
name = "demo-cluster"
vpc_zone_identifier = ["${aws_subnet.demo-public-1.id}", "${aws_subnet.demo-public-2.id}", "${aws_subnet.demo-public-3.id}"]
min_size = "2"
max_size = "10"
desired_capacity = "2"
launch_configuration = "${aws_launch_configuration.demo-cluster-lc.name}"
health_check_grace_period = 120
default_cooldown = 30
termination_policies = ["OldestInstance"]
tag {
key = "Name"
value = "ECS-demo"
propagate_at_launch = true
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_policy" "demo-cluster" {
name = "demo-ecs-auto-scaling"
policy_type = "TargetTrackingScaling"
estimated_instance_warmup = "90"
adjustment_type = "ChangeInCapacity"
autoscaling_group_name = "${aws_autoscaling_group.demo-cluster.name}"
target_tracking_configuration {
predefined_metric_specification {
predefined_metric_type = "ASGAverageCPUUtilization"
}
target_value = 40.0
}
}
resource "aws_launch_configuration" "demo-cluster-lc" {
name_prefix = "demo-cluster-lc"
security_groups = ["${aws_security_group.instance_sg.id}"]
# key_name = "${aws_key_pair.demodev.key_name}"
image_id = "${data.aws_ami.latest_ecs.id}"
instance_type = "${var.instance_type}"
iam_instance_profile = "${aws_iam_instance_profile.ecs-ec2-role.id}"
user_data = "${data.template_file.ecs-cluster.rendered}"
associate_public_ip_address = true
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
}
And our ecs-cluster.tpl file
#!/bin/bash
echo ECS_CLUSTER=${ecs_cluster} >> /etc/ecs/ecs.config
Next we add our ECS service and task and Cloud Watch configurations.
ecs-nginx.tf
# NGINX Service
resource "aws_ecs_service" "nginx" {
name = "nginx"
cluster = "${aws_ecs_cluster.demo.id}"
task_definition = "${aws_ecs_task_definition.nginx.arn}"
desired_count = 4
iam_role = "${aws_iam_role.ecs-service-role.arn}"
depends_on = ["aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.ecs-service-attach"]
load_balancer {
target_group_arn = "${aws_alb_target_group.nginx.id}"
container_name = "nginx"
container_port = "80"
}
lifecycle {
ignore_changes = ["task_definition"]
}
}
resource "aws_ecs_task_definition" "nginx" {
family = "nginx"
container_definitions = <<EOF
[
{
"portMappings": [
{
"hostPort": 0,
"protocol": "tcp",
"containerPort": 80
}
],
"cpu": 256,
"memory": 300,
"image": "nginx:latest",
"essential": true,
"name": "nginx",
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "/ecs-demo/nginx",
"awslogs-region": "eu-west-2",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "ecs"
}
}
}
]
EOF
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_group" "nginx" {
name = "/ecs-demo/nginx"
}
Next on the list is to add the IAM roles for the EC2 intances so they can communicate with the ECS service.
iam.tf
# ecs ec2 role
resource "aws_iam_role" "ecs-ec2-role" {
name = "ecs-ec2-role-test"
assume_role_policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": ""
}
]
}
EOF
}
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "ecs-ec2-role" {
name = "ecs-ec2-role-test"
role = "${aws_iam_role.ecs-ec2-role.name}"
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "ecs-ec2-role-policy" {
name = "ecs-ec2-role-policy-test"
role = "${aws_iam_role.ecs-ec2-role.id}"
policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecs:CreateCluster",
"ecs:DeregisterContainerInstance",
"ecs:DiscoverPollEndpoint",
"ecs:Poll",
"ecs:RegisterContainerInstance",
"ecs:StartTelemetrySession",
"ecs:Submit*",
"ecs:StartTask",
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
]
}
]
}
EOF
}
# ecs service role
resource "aws_iam_role" "ecs-service-role" {
name = "ecs-service-role-test"
assume_role_policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ecs.amazonaws.com"
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": ""
}
]
}
EOF
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "ecs-service-attach" {
role = "${aws_iam_role.ecs-service-role.name}"
policy_arn = "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AmazonEC2ContainerServiceRole"
}
Next we have our security groups. From here we can observe that the load balancer is open to the world on tcp/80 and tcp/443 and the ECS EC2 instances have ports 32768 to 65535 open from the load balancer. This is because when we select the container port to 0 in the task definition AWS will randomly assign a port from this range to the container.
security.tf
resource "aws_security_group" "lb_sg" {
description = "controls access to the application ELB"
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
name = "demo-ELB"
ingress {
protocol = "tcp"
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
protocol = "tcp"
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = [
"0.0.0.0/0",
]
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "instance_sg" {
description = "controls direct access to application instances"
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.demo-tf.id}"
name = "application-instances-sg"
ingress {
protocol = "tcp"
from_port = 32768
to_port = 65535
description = "Access from ALB"
security_groups = [
"${aws_security_group.lb_sg.id}",
]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
Lastly we have our variables file. Here you can change your region and the instance type you decide to use.
vars.tf
variable "aws_region" {
description = "The AWS region to create things in."
default = "eu-west-2"
}
variable "instance_type" {
default = "t2.large"
description = "AWS instance type"
}
So now it’s time to run terraform apply
We should get an output with the address of the load balancer
aws_alb_listener.front_end: Creation complete after 0s (ID: arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:eu-west-2:...-alb/c08966d3a19dd606/268a2724c5840005)
aws_ecs_service.nginx: Creation complete after 1s (ID: arn:aws:ecs:eu-west-2:623844463527:service/nginx)
Apply complete! Resources: 29 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
alb_output = demo-eu-alb-1234567890.eu-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com
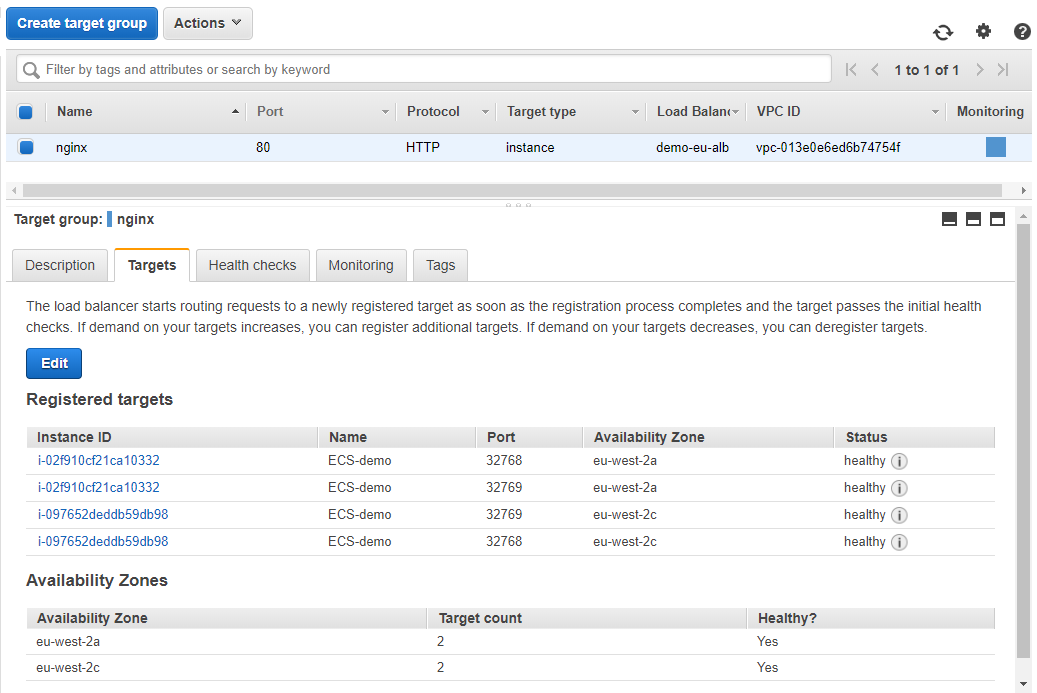
So now if we head over to our target group in AWS we can see that we have 4 healthy running tasks all listining on the same port (tcp/80) balanced evenly across two separate instances.
Don’t forget to run terraform destroy if you are just learning this.