In this post we are going to create an S3 bucket with a random name using the Terraform format function.
As usual we have our provider block.
# Provider
provider "aws" {
region = "eu-west-1"
}
Next we create a random string with the resource "random_id" 5 random bytes which produces 12 bits of randomness.
# Create a random string
resource "random_id" "random_string" {
byte_length = 5
}
Next we create a variable for the bucket name
# Bucket name
variable "bucket_name" {
type = string
default = "letslearndevops"
}
Next we create the bucket.
The line we’re really interested in is the bucket line where we use the format function. Here we’re using %s which is used to convert to string and insert the string’s characters and %d which converts to integer number to produce decimal representation.
# Create the bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "letslearndevops_bucket" {
bucket = format("%s-%d",var.bucket_name, random_id.random_string.dec)
acl = "private"
force_destroy = true
}
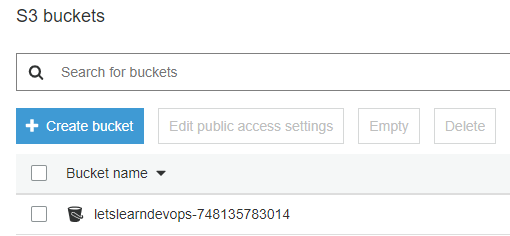
The result is as expected, a new S3 bucket with a random 12 character string appended to the bucket name.
Now lets add some tags to the same bucket
# Create the bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "letslearndevops_bucket" {
bucket = format("%s-%d", var.bucket_name, random_id.random_string.dec)
acl = "private"
force_destroy = true
tags = {
String = "String"
Name = format("%s", var.bucket_name)
Creation_Date = format("%s", formatdate("DD MMM YYYY", timestamp()))
}
}
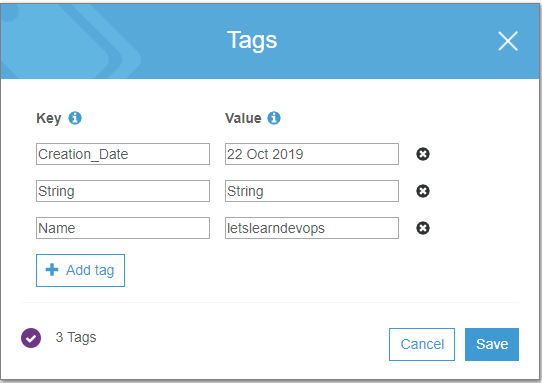
With the following result.
Here you can see the String key is just defined as a simple "string", the Name key uses the format function to call var.bucket_name and the Creation_Date key used the timestamp function which is then formatted using the formatdate function.